Turbocharger defective? Repair or change?
Content
1. How the turbocharger works in the car
2. Turbocharger repair or replacement?
3. Symptoms of a defect in the turbocharger
An exhaust gas turbocharger helps the engine to produce more power and improves fuel economy. Numerous manufacturers therefore use a turbocharger in their models. However, this also provides the car with another component that can break down. The question that often arises in the workshop is whether to repair or replace the turbocharger. In our guide, you will learn about the advantages and disadvantages of each and how to replace the turbocharger.
How the turbocharger works in the car
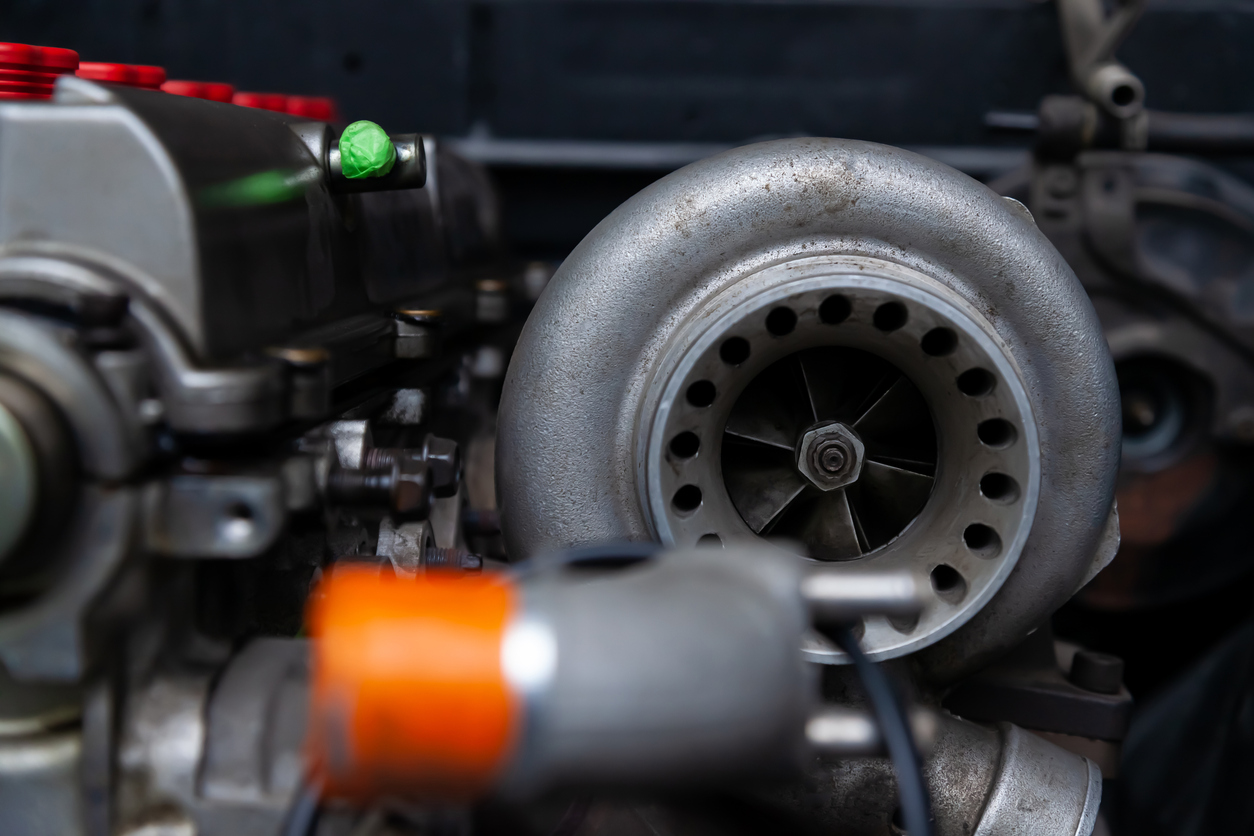
Many cars are equipped with an exhaust gas turbocharger. This component feeds fresh air to the engine at a certain boost pressure. This leads to a higher output with the same displacement. In modern engines, the turbo reduces fuel consumption.
Charger is driven by the exhaust gas
The turbocharger is driven by the engine’s exhaust gas flow and has a turbine wheel for this purpose. The turbine is rigidly connected to a compressor wheel inside the turbo, which compresses the air before combustion and feeds it to the engine.
Turbocharger repair or replacement?
Defective turbochargers are usually replaced completely. However, it is also possible to repair the turbocharger. When turbocharger damage occurs, car owners are often faced with a difficult decision. Turbocharger repair or replacement of the entire component? Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages. If you are undecided, you should ask the workshop for an estimate of the cost of repairing or replacing the turbocharger.
Repair of the turbo by a professional
Checking and repairing turbochargers requires specialist knowledge and experience. Very few car mechanics therefore want to carry out the repair of the turbocharger themselves. Some specialist companies, on the other hand, have specialised in the repair of turbos. They have all the necessary machines for testing and the necessary know-how. Thus, the specialists carry out an overhaul of the turbocharger with components of high quality.
Replacing the turbocharger
Many workshops favour replacing the turbo with a new component. In some cases, this approach can save high costs. This is because the complete repair, including removal and turbocharger installation, can be carried out in just one day. New turbochargers from the original manufacturer or spare parts of high quality can be installed according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Symptoms of a defect in the turbocharger
If the turbocharger is defective, various signs may indicate the fault. These include a noticeable drop in engine performance or unusual noises from the turbocharger. Smoke from the exhaust or high oil consumption can also occur. In some cases, the vehicle goes into emergency mode if the turbocharger is defective.
The symptoms at a glance
- Engine performance has noticeably decreased
- Boost pressure drops sharply
- Smoke from the exhaust
- Noise from the turbocharger
- Vehicle jumps into the emergency programme
- Oil consumption is rising steadily
Have the turbocharger checked and repaired at an early stage
As soon as the first signs indicate that the turbocharger could be defective, the problem should be checked more closely. If the symptoms are ignored, major damage to the turbo can quickly occur. In many cases, repair is then expensive or no longer possible. Driving with a defective turbocharger can also cause engine damage.

Causes for defects on the turbocharger
If the turbocharger is defective, there are various possible causes. High mileage causes a certain amount of wear on the turbo, and a sporty driving style also causes the turbocharger to wear out more quickly. Often the turbo is broken because it was not sufficiently lubricated due to a lack of oil or because the wrong oil was filled in. In addition, foreign bodies in the intake tract can damage the compressor wheel.
Overview of common causes
- Turbocharger wear
- Turbo damage due to sporty driving style
- Lack of oil on the turbo
- Oil type was filled in incorrectly
- Foreign body in the intake tract
Changing the turbocharger
If the turbo causes problems, the turbocharger repair should not be put on the back burner. Removal of the turbocharger is indispensable. It is irrelevant whether a turbocharger replacement is planned or whether the turbo is to be sent for repair. Experienced and skilled hobby mechanics often carry out the removal and installation of the turbocharger themselves in order to save costs for the workshop.
Turbocharger change duration
How long it takes to change the turbocharger depends on various factors. Depending on the engine and the respective vehicle model, the work can take more or less time. If you want to change the turbocharger yourself, you should always allow enough time. If you want to have the turbocharger installed, you can contact various workshops in advance to estimate the time and costs involved.
Turbocharger change instruction
Depending on the vehicle model, a specific approach may be necessary to change the turbocharger. In some cases, the turbo is better removed from above, in others from below the engine compartment.
The all-important question is: Where is the turbocharger located? Depending on the model, the turbocharger may be hidden in the engine compartment. In this case, numerous other components have to be removed in order to change the turbocharger.
Changing the turbocharger in 5 steps
- Prepare for removal: Before the actual removal of the turbocharger can begin, the procedure must be prepared. In many cases, this involves dismantling all the trim parts in the engine compartment as well as numerous components, such as parts of the exhaust system. As a rule, the oil and, in the case of turbochargers with water cooling, the water must also be drained.
- Remove the turbocharger: In the second step, the defective turbocharger can be removed. To do this, all connections on the turbocharger must be loosened and the connected lines removed. Then the turbocharger itself is detached from its fastening points.
- Remove the turbo: Once all lines and screws of the turbocharger have been loosened, it can usually be removed from the engine compartment without any problems. Any leaking operating fluids such as oil or coolant must be collected and disposed of accordingly. The turbocharger can then be visually inspected and, if necessary, sent for repair.
- Prepare for installation: Before installing a new or repaired turbocharger, it is essential to clarify the cause of the defect in the old turbocharger. Only when this has been eliminated can the installation begin. Before the intact turbocharger can be installed, it must often be fitted with the necessary attachments.
- Install the turbo: Before installation, the turbocharger is briefly visually inspected. However, new turbochargers from current production of the manufacturer or from a reliable source are usually in perfect condition. In addition, the connecting lines in the engine compartment should be checked and cleaned or replaced if necessary. Finally, the turbocharger is installed in reverse order.
Top guides
- Injection system in the car explained simply - parts and function of the injection...
- Maintenance and repair of electric cars: what can your normal garage do?
- Increasing performance with chip tuning: benefits, risks and tips
- Guide: Computer systems and software in your car
- Which electric car parts need repair or replacement most often?
- What is a solid-state battery for electric cars?
- All about engine sensors: from combustion engines to electric cars
- Increase the range of an electric car: How every electric car gets further
- Electric car battery life: How to extend the life of the battery
- What is the compression of a car engine?
- This is the cubic capacity of a car engine
- Internal combustion engine valves: function, defects and repair
- Core components of the internal combustion engine - parts and functions
- Engine lubrication in cars: components, function and defects
- The environmental impact of manufacturing new car parts
- All about pollutant classes and their role in environmental protection
- Engine overhaul: What is an engine overhaul and how much does it cost?
- OEM car parts manufacturing: the key components of the sector
- Understanding engine power - insight into the technology of the car engine
- The steering system of the car - structure and operation
- The car's braking system - structure, parts and function
- Engine types in the car: V-engine, in-line engine and boxer engine explained
- 8 tips before buying a used electric car
- Distinguish OEM parts, aftermarket and counterfeit car parts
- The EPC indicator light is on or flashing: What to do?
- Master brake cylinder: function, defect detection and repair
- OEM car parts for hybrid and electric cars
- Used youngtimer and classic car parts - the best tips
- Cruise control: Function and repair of the cruise control system in the car
- Exhaust system: Everything you need to know about parts and function of the exhaus...
- Locking system: security and reliable locking on the car
- The engine's air intake system - parts, function and replacement
- Brake caliper defective? How to replace it yourself
- Fuel system: parts of the fuel supply from the tank to the cylinder
- Air conditioning system: function and components of your car air conditioning syst...
- The clutch: structure and function explained simply
- Detecting and replacing a defective fuel pump
- Surprised? So many pumps work in your car
- The most common causes of a defective electric car
- The 6 most important safety components of your car
- Identify and repair a defective starter in a flash
- 5 common chassis problems and how to fix them
- 10 unknown car parts that many drivers do not know about
- Engine cooling: function and important components of the cooling system
- Differences between petrol and diesel engines
- All-wheel drive: How the mechanics and components of all-wheel drive work
- Engine control unit car: Everything about components and functioning
- Defective engine control unit: causes, symptoms and repair
- HP vs. torque: What is the difference between power and torque?
- EV motors basics: How are they built, how they work and differ from combustion eng...
- The chassis: overview and function of all suspension components
- Used electric car parts: What to look out for
- The importance of the chassis number when buying used car parts
- ABS pump defective? Function, repair and replacement
- Injection nozzle defective? Diagnosis, cleaning and changing the injection nozzles
- Alternator defective? What symptoms occur and when to change the component
- Water pump defective? Symptoms and how to repair or change it
- Steering gear defective? What are the symptoms and when should the component be re...
- Lambda sensor defective? What are the symptoms and can I clean the sensor?
- Defective air conditioning compressor - what are the symptoms and when should the ...
- Intake manifold defective? Replace gasket or clean manifold?
- Exhaust manifold leaking? Symptoms of a defective exhaust manifold or gasket and w...
- Turbocharger defective? Repair or change?
- Servo pump defective? What symptoms occur and when you should change the part
- Clutch broken? - These symptoms indicate a defect in the clutch
- Common problems and repair of defective drive shafts
- Causes of engine noise and what to do about it?
- What can car diagnostic devices do and do I need an OBD scanner?
- When and how to replace brake discs and brake pads
- Brake warning lamp lights up - causes and what to do?
- EGR valve defective: Avoid engine problems and clean EGR valve
- Improve fuel consumption: How your car uses less fuel
- Squeaking brakes: Why brakes squeak and how to get rid of it
- Safely jacking up a car: How to jack up a car using a jack and jack stands
- How a defect in the muffler becomes noticeable and how it is replaced
- E-car motor: These electric car parts you can replace yourself
- Engine overheated: What you should do if the engine overheats
- Engine check lamp lights up: What you should do as a motorist
- The engine code: What does the code mean and where can I find it on the car?
- Tools for car repair: These 10 tools you should own
- Car repair mistakes: These are the 7 most common car repair mistakes
- The gearbox code: What does the code mean and where can it be found on the gearbox...
- Used parts: How to check the quality of used car parts
- Vehicle transmission: What is the difference between manual and automatic transmis...
- Mileage: This is how mileage affects used spare parts
- Car recycling: What happens to the car when it is recycled?
- OEM original parts or aftermarket: these are the differences
- Advantages and disadvantages of new and used car parts
- Starting problems? Top 9 reasons why your car does not start
- What’s that smell from my car? Top causes and cures
- Advantages of shopping scrap car parts online vs. going to the local breaker yards...
- 10 most frequently purchased car parts from car breakers/junkyard
- Important car parts and their function
- Common car engine problems: Diagnosing, Troubleshooting and Fixes
- Best tips for setting up your own home car workshop
- 7 Car parts replacements and repair tasks you should not do yourself
- DIY Car Maintenance and Repair Tasks
- Guide: How to Maintain and Protect Your Car Engine
- Best practices for Engine Rebuild
- Common Causes of Rear Differential Noise, troubleshooting, and how fix it
- Common Causes of power steering noise and how fix it
- Your Guide to Car Engine Components and Functions
- Licence plate and VIN information
- Top 10 of the most popular brands in second-hand autoparts
- France is just so cool